HDPE vs UHMWPE in the Factory: A Machinist’s Guide to the Best Fit for Your Parts

🔥 Machinist's Exclusive Offer: Use code QR4GNY08SHVR at checkout for a special discount on your entire order! 👉 Shop UHMWPE & Acrylic
In any machining environment, the materials you choose are as critical as the tools you use. When you're selecting between HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) and UHMWPE (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene), understanding their real-world behavior on the factory floor is key to machining efficiency, part durability, and long-term performance.
As a machinist or production engineer, you need more than datasheets—you need insights from practical applications. Whether you're working to reduce tool wear, improve turnaround time, or avoid unnecessary part replacements, this guide helps you determine which plastic gives your parts the edge they need.
Choosing the right thermoplastic material is like choosing the right cutting tool—it affects everything from finish quality and lead time to maintenance cycles and equipment longevity. As industries push for faster production, lighter materials, and extended part lifespan, polyethylene-based plastics have emerged as the go-to solution in environments demanding versatility, chemical resistance, and mechanical performance. HDPE and UHMWPE are two standouts in this category, but while they may look similar at a glance, their machining behavior, wear resistance, and suitability under pressure diverge in critical ways.
Machining Matters: How HDPE and UHMWPE Perform on the Shop Floor
| Feature | HDPE | UHMWPE |
|---|---|---|
| Machinability | Excellent (Crisp edges) | Requires Finesse |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Superior |
HDPE is widely appreciated for its ease of fabrication. It responds beautifully to standard CNC milling and turning, producing crisp edges, minimal burrs, and predictable chip patterns. Most machinists find HDPE forgiving, with low tool wear, excellent cut consistency, and a surface finish that often requires minimal post-processing. It's ideal for high-throughput jobs where speed and reliability are paramount.
UHMWPE, however, demands more finesse. Its slippery, low-friction nature means it can shift or deform slightly during machining if not properly secured. It also has a tendency to develop heat if machined too aggressively, which may compromise dimensional accuracy. But with sharp tooling, lower RPMs, and refined feeds and speeds, machinists can produce parts with exceptional wear properties that will outlast most alternatives. While HDPE may save you time at the spindle, UHMWPE can deliver years of value in use.

Figure 1: Comparison of polyethylene standard stock forms.
Wear Resistance and Longevity: Which One Lasts Longer?
When you need parts to stand up to daily punishment, UHMWPE leads the charge. With a coefficient of friction lower than most plastics, and even some metals, UHMWPE dramatically reduces the wear caused by repeated contact or motion. Components made from this material can absorb shock loads, resist abrasion, and operate quietly without lubrication.
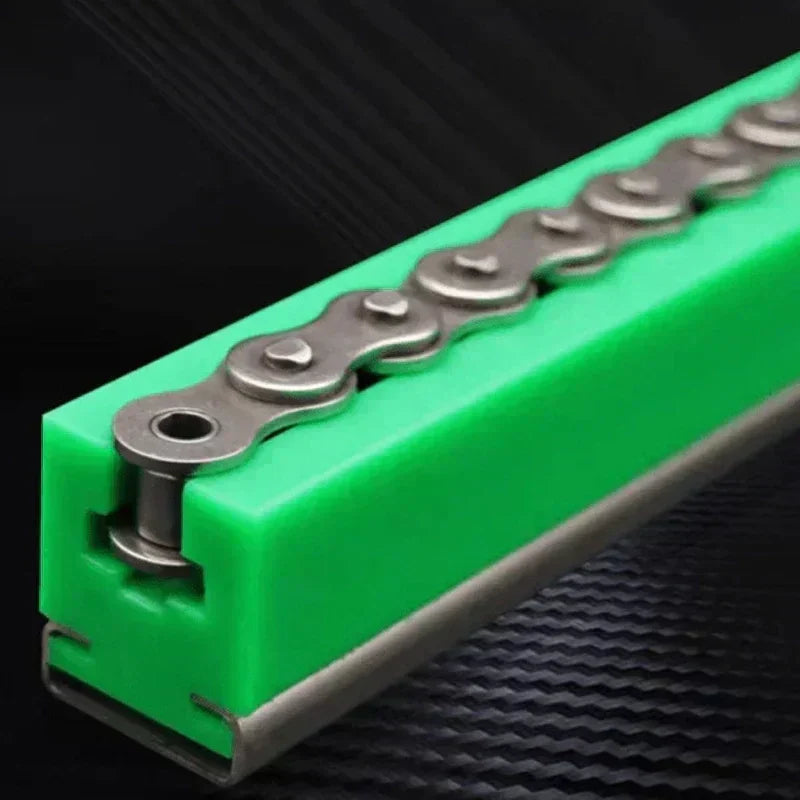
This makes UHMWPE ideal for components like conveyor rails, wear strips, chute liners, and high-speed guide elements. In these applications, long service life directly translates to fewer replacements, less downtime, and higher efficiency.

HDPE still plays an important role in environments where parts are static or face minimal mechanical contact. It has solid impact resistance, can flex slightly under load without cracking, and remains chemically stable over time. For parts like chemical tank fittings, enclosures, or mounting panels, HDPE offers a cost-efficient balance of strength and ease of production.
Cost vs. Value: What’s the Smart Spend?
HDPE is clearly the more economical option upfront. It’s not only less expensive per pound, but it also machines faster, creating lower labor costs and tool wear. That makes it the material of choice for short runs, prototype work, or projects where price sensitivity matters more than endurance.
But when failure isn’t an option—or when replacement involves halting production—UHMWPE shines. Its higher initial cost is balanced by its ability to last much longer, especially in moving or load-bearing roles. In fact, many manufacturers consider it a long-term investment: instead of replacing HDPE parts every 6–12 months, a well-machined UHMWPE part might last two years or more under identical conditions.
The smartest spend is based on lifecycle thinking. Ask yourself: What’s the true cost of a failed part? How much time and money does your team spend on replacements, troubleshooting, or unplanned maintenance? If longevity matters, UHMWPE often becomes the more economical choice in the long run.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance: Working Conditions Matter
Both materials hold up well to a variety of industrial chemicals, but UHMWPE offers a broader spectrum of compatibility and long-term durability. HDPE resists many diluted acids and alcohols, and it’s FDA-approved for food contact, which makes it common in packaging, agricultural, and food production settings.
UHMWPE goes further. It resists even concentrated acids and strong bases. It also retains its properties in freezing conditions and humid environments, where some plastics might become brittle or soften. That makes it especially useful in outdoor, marine, and pharmaceutical environments where exposure to aggressive agents is frequent.
In short, if your plant runs in a high-humidity, chemically aggressive, or highly variable temperature range, UHMWPE is better engineered for consistency and reliability.
Practical Recommendations: Which Plastic Fits Which Part?
Selecting the right material often comes down to asking the right questions about application needs, operational cycles, and tolerances for failure. Here’s a breakdown based on functionality and environment:
- Structural components and industrial panels
- Pipe fittings, tanks, and reservoir walls
- Food-grade machine guards
- Cost-driven projects or early-stage prototyping
- High-wear parts under dynamic load (sliders, glides, cams)
- Conveyor tracks, guide rails, and robotic assembly lines
- Sub-zero or chemically aggressive environments
- Any application where lubrication is limited
Every factory setup is different. Your ideal solution will depend on what you're producing, how it moves, and how long it needs to last.

Figure 2: Custom machined UHMWPE industrial parts.
Need Custom Parts Machined?
We provide CNC plastic milling, turning, and cut-to-size services for both HDPE and UHMWPE. No minimum quantity required.
Explore CNC Machining Services →Built to Perform: Choose the Right Plastic and Cut with Confidence
🎉 Limit Time Offer
Equip your factory floor with premium UPE and Acrylic plastics. Don't miss out on this week's efficiency boost.
Shop Now & Save →
-
Posted in
cnc plastic machining, factory plastic selection, HDPE, hdpe vs uhmwpe, industrial plastic parts, machinable plastic, plastic materials, polyethylene, uhmw plastic properties, uhmwpe, wear resistant plastic