Exploring the World of PP Plastic: Unveiling Its Properties and Diverse Applications

Polypropylene (PP) plastic is one of the most widely used thermoplastics in the world today. With its unique combination of physical, chemical, mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, polypropylene plastic has revolutionized various industries from packaging to automotive, becoming an indispensable material in modern world.
🎉🎉🎉Limited Time Offer Use code: QR4GNY08SHVR at checkout and enjoy a special discount on your entire order! 👉PP board
It is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of PP plastic material including its characteristics, capabilities, and applications. This article will provide an in-depth exploration of polypropylene, unveiling what makes it such a versatile and high-performance plastic.

II. What is PP Plastic?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer made by polymerizing propylene monomers in presence of organometallic catalysts. The propylene monomers are derived from fossil fuel sources like natural gas and petroleum.
Chemically, PP polymer has a backbone chain of carbon atoms with attached hydrogen atoms. The absence of branched chains gives PP material strength and stiffness. The chemical structure also grants it resistance to various solvents and acids.
Compared to other widely used plastics like polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene plastic is more rigid and heat resistant. Its higher melting point allows polypropylene to retain strength even at elevated temperatures.
III. Key Properties of PP Plastic
Polypropylene properties make it suitable for numerous applications:
Polypropylene Strength and Durability
With high tensile strength and modulus of elasticity, PP plastic resists deformation under load. This durable PP material retains shape even after repeated use. The uniform structure also minimizes cracks from stress concentration.
PP Plastic Flexibility and Heat Resistance
Despite rigidity, PP plastic has good impact strength aided by micro-crystallinity. This PP polymer flexibility allows bending without fracturing. With high melting point (~320°F/160°C) and glass transition temperature, polypropylene retains mechanical strength even when exposed to temperatures over 200°F (93°C).
Chemical Resistance and Safety Features of PP Material
PP plastic offers high resistance to acids, bases, and solvents - especially at lower temperatures. This PP material prevents corrosion and maintains integrity of containers exposed to chemicals. Unreactive surface also ensures polypropylene safety when in contact with food or medical contents.

IV. Diverse Applications of PP Plastic
Owing to the beneficial properties, polypropylene has diverse applications:
PP Plastic in Packaging: Revolutionizing the Industry
With high rigidity balanced by impact, tensile and flexural strength, PP plastic makes excellent packaging material. As a PP polymer, it provides mechanical stability to products while being lightweight for efficiency demands of the packaging industry. Its inertness also allows safe storage of edibles and pharmaceuticals.

Automotive Applications: How PP Material Contributes to Vehicle Manufacturing
In automotive industry, PP plastic gets molded into interior and exterior components like battery cases, cables, gearbox, bumpers etc. The durable PP material resists wear & tear from mechanical forces. Resistance to vibrational fatigue enables use of polypropylene in avenues with rapid motion.
Polypropylene in Textiles: A New Era of Fabric Innovation
PP plastic can be made into synthetic fibers alone or blended with cotton/wool. Fabrics made from PP polymer demonstrate dyeability, comfort and mechanical characteristics like elasticity and durability. Easy to clean and insulative properties expand polypropylene usage into sportswear and carpets.
PP Polymer in Medical Devices: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency
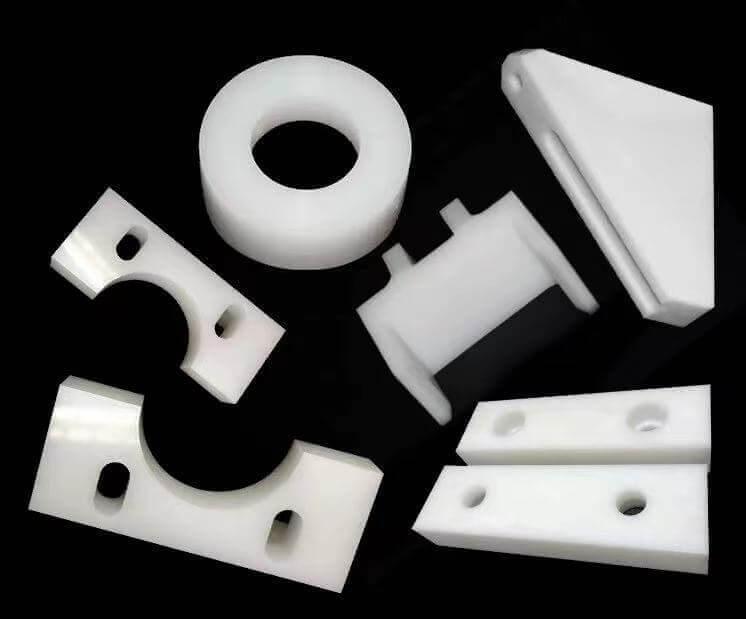
Owing to biocompatibility, sterilizability and rigidity - polypropylene makes for widely used medical plastics. PP plastic gets crafted into syringes, sample containers, surgical tools which can withstand repeated steam sterilization and UV irradiation. With high precision moldability, it is shaping high-performance medical devices.

Consumer Goods and Industrial Use: The Versatility of PP Plastic
Daily appliances routinely feature polypropylene due to its balance of properties, processability and cost-effectiveness. The PP material has been transformed into toys, household containers, car interiors. Its low moisture absorption allows extensive use of the plastic in piping, slurry tanks. PP plastic is also recycled into non-critical application sectors.
V. Advantages of Using PP Plastic
Using polypropylene confers multiple advantages:
The Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability of PP Material
Polypropylene plastics strike the optimal balance of performance and production costs. Easy moldability into variety of geometries makes PP plastic ideal for mass manufacturing. As a high-volume engineering material, recycling initiatives allow reusing scrap/waste plastic into value-added products ensuring sustainable PP materials.

Environmental Impact: PP Plastic Recycling and Eco-Friendliness
PP plastic is highly recyclable, and recycled polypropylene offers properties near virgin material. With rising adoption of polypropylene (expected CAGR 5.8%), recycling is crucial. PP material recycling significantly reduces carbon footprint by lowering new plastic production. This eases landfill burden making it an eco-friendly plastic.
High-Performance PP Plastics: Meeting Modern Demands
With active research into new catalysts and polymerization processes, technologists are developing high-performance grades of PP plastic. These advanced materials display improved temperature capabilities, clarity and can compete with engineering thermoplastics. The 21st century will see wider adoption of such high-performance PP plastics in multiple sectors.
VI. Innovations in PP Plastic Manufacturing
Polypropylene manufacturers are invested into expanding capabilities:
Advanced PP Polymer Applications: Breaking New Ground
Using novel polymerization and processing methods, companies are making foams, large 3D printed parts and precision-molded micro-plastics with superior isotropy, surface quality and consistency. With these advanced PP polymer applications, engineers can deploy polypropylene into aviation components and pharmaceutical equipment sectors.
The Future of PP Material: Trends and Potential Developments
Insights into polymer blending and reinforcement by nanoscale additives will further strengthen PP plastic in times to come. Biodegradable polypropylene which breaks down faster is being investigated. light-weight foams and porous plastic variants will help design efficient automotive parts with the PP material. There remains vast scope for innovation in polypropylene types.

VII. Conclusion
In summary, polypropylene plastics display a versatile range of properties (high temperature stability, impact balance and chemical inertness) which lend them useful in packaging, textiles, automotive and medical domains. With active research into advanced materials, and recycling practices scaling globally - the appreciation for polypropylene capabilities and sustainable advantages continues rising, benefiting industrial ecosystems. Understanding the science behind the material aids application what PP plastic products can enable next.
🎉🎉🎉Limited Time Offer Use code: QR4GNY08SHVR at checkout and enjoy a special discount on your entire order! 👉PP board